Integrating Vercel with Checkly
If you are using Vercel to develop, preview, and ship your application, you can natively integrate with Checkly by installing the official integration from the Vercel Marketplace.
Checkly offers two integration paths:
- Native integration, if you don’t yet have a Checkly account. With the native integration, user access and billing is managed through Vercel. If you are new to Vercel’s native integrations you can read more about them on the Vercel documentation page.
- Connected integration, if you already have a Checkly account. The connected integration can be installed on top of the native integration for the full Checkly - Vercel integration experience.
The Vercel integration will help you by:
- Automatically creating a pre-scripted browser check to catch any errors and failed requests as your web page loads.
- Enabling you to run checks against preview and production deployments on Vercel.
Using Vercel deployment protection? Read this section on how to make this work with Checkly.
Installing the native integration
To install Checkly’s managed Vercel integration, navigate to the integration’s marketplace listing and click Install.
- Select
Create new accountin the installation guide and clickNextto accept the terms and conditions. - Select your plan type. You can read about our pricing plans here, and more about how we bill checks here.
- Name your account and review your plan selection. You can change your account name later.
- Press
Createto continue to the integration settings page. SelectGetting startedto go to the setup guide in Vercel. You can also clickOpen in Checklyto go through the Checkly + Vercel onboarding and get you started with an example project showcasing how to use Monitoring as Code together with Vercel. You can also jump straight to our example NextJS project which includes a guide on how to use Monitoring as Code with a NextJS project. - If you want to directly connect your Checkly checks with Vercel and run them against preview and deployments on Vercel, continue with installing the connected integration, as explained below.
Installing the connected integration
-
To install Checkly’s connected Vercel integration, navigate to
Integrations, under your account’s dropdown menu and click theVercel marketplacebutton, or go directly to the integration listing on the Vercel marketplace. -
On the marketplace page for Checkly, click
Connect Account. -
Next, follow the installation wizard to grant the integration access to the right Vercel scope and projects.
-
You can choose to map your Vercel projects to existing checks on your Checkly account, to have them run on production and/or preview deployments.
-
Additionally, you can have new checks automatically generated for existing Vercel projects, and set them up to automatically run on preview and/or production deployments.
Linking checks and groups with the connected integration
If you already have the connected Vercel integration set up, you might still want to connect new checks or groups. The procedure is the same for both: edit the check or group and select Vercel in the Testing tab, then select Link Vercel project and the project you want to link.
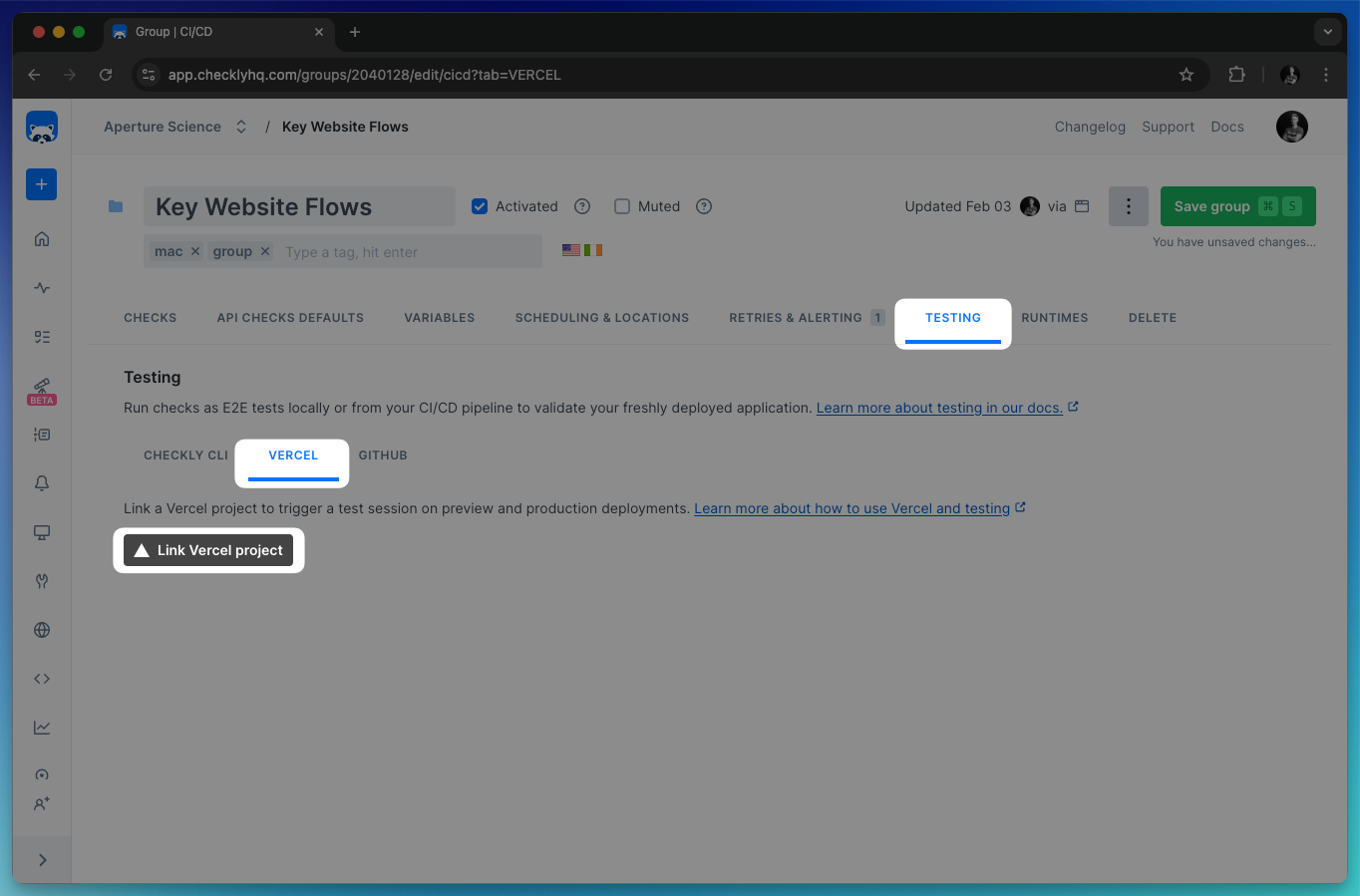
Once the project and the check/group have been linked, you are able to specify whether a new preview or production deployment should trigger a new execution. You will also have the chance to choose from which location this check will run.
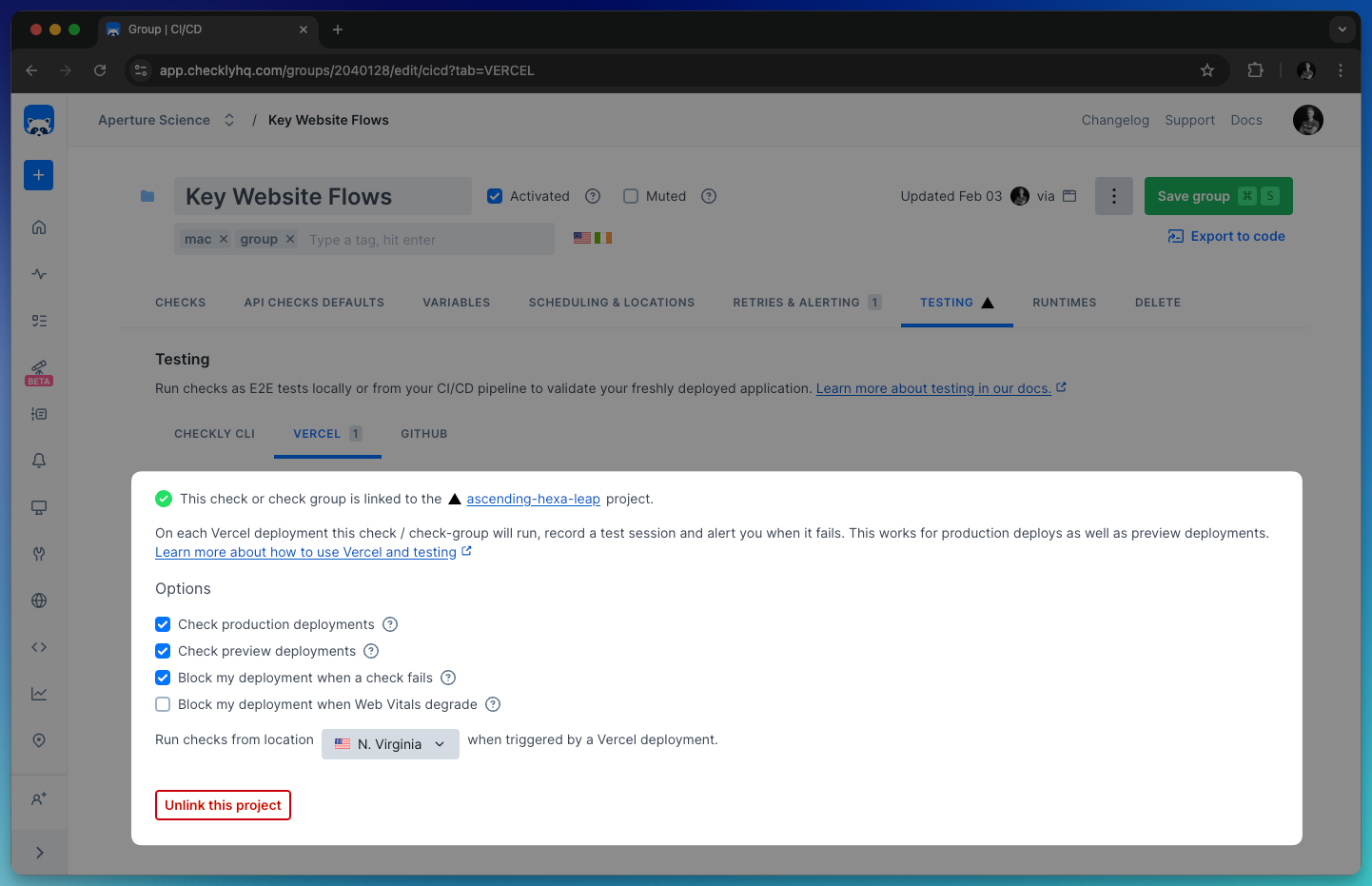
Should you wish to unlink the Vercel project, simply click Unlink this project.
Targeting Preview deployments with ENVIRONMENT_URL and ENVIRONMENT_NAME
On each deployment triggered by Vercel, we inject the Checkly runtime with two variables:
ENVIRONMENT_NAME: This name ispreviewfor preview deployments andproductionfor production deployments.ENVIRONMENT_URL: For Preview deployments this is the preview URL alias, e.g.https://ecommerce-1wabp0sqy-acme.vercel.app, for Production deployments it is the equivalent production URL alias.DEPLOYMENT_ID: The unique deployment ID generated by Vercel.
You can access all these variables with the familiar process.ENV syntax.
Browser checks
This means you can write a Browser check using Playwright Test or Playwright that automatically targets the Preview deploy whenever this URL is available, but otherwise just defaults to the stable production URL.
Here is a full example that we use ourselves to monitor checklyhq.com which is actually also deployed to Vercel.
import { expect, test } from '@playwright/test'
test('assert response status of page', async ({ page }) => {
const targetUrl = process.env.ENVIRONMENT_URL || 'https://www.checklyhq.com'
const response = await page.goto(targetUrl)
expect(response.status()).toBeLessThan(400)
})
const { expect, test } = require('@playwright/test')
test('assert response status of page', async ({ page }) => {
const targetUrl = process.env.ENVIRONMENT_URL || 'https://www.checklyhq.com'
const response = await page.goto(targetUrl)
expect(response.status()).toBeLessThan(400)
})
This way we are setting the targetUrl variable to either the ENVIRONMENT_URL or just our main production URL.
Whenever a Preview deploy happens on Vercel, this check gets called and runs the script against the preview environment. This check also runs on a 5 minute schedule, and checks our production environment.
This way, we kill two birds with one stone and don’t need separate checks for separate environments.
API checks
With API checks, we automatically replace the hostname part of your request URL with the host in the environment URL. For example:
- Your configured URL: https://api.acme.com/v1/customers?page=1
- Environment URL: https://now.customer-api.qis6va2z7.now.sh
- Replaced URL: https://now.customer-api.qis6va2z7.now.sh/v1/customers?page=1
Notice we only replace the host part, not the URL path or any query parameters.
Just like for browser checks, the check will run on deploy against our preview environment, while also still running on a schedule against production.
How Checkly checks maps to Vercel checks
Checkly integrates deeply with the Vercel Checks functionality API to link Checks in both tools. Vercel uses a slightly different way in representing checks than Checkly does, specifically splitting individual check results into either:
- Reliability checks
- Performance checks
This is how a Checkly check maps to a Vercel check:
- API checks are always mapped 1:1 and marked as a Reliability check.
- Browser checks are split into a Performance and Reliability check, where the Performance part is populated with Web Vitals data*.
- Groups of checks are “unfolded” in the Vercel user interface and all checks are shown individually.
* Web Vitals are only recorded for Playwright-based Browser checks
Blocking Vercel deployments
You can block your Vercel deployments if any of your checks fail or if the web vitals degrade:
- Block my deployment when a check fails does what it says on the tin and only applies to Vercel Reliability checks.
- Block my deployment when Web Vitals degrade is a bit special and only applies to Vercel Performance checks for our Browser checks.
This table will help you determine how blocking checks works. Note — again — that Browser checks, can fail a Vercel deployment in two ways because the Reliability part and Performance part are evaluated separately.
| Checkly | Vercel | Blocking heuristic |
|---|---|---|
| API Check | Reliability Check | Blocks deployment when it fails due to > 399 HTTP response codes, assertions and other API check specific features. |
| Browser Check | Reliability Check | Blocks deployment when it fails due to > 399 HTTP response codes on the main HTML document, syntax errors in the script, or assertions using the expect or assert libraries in the browser check script. |
| Performance Check | Blocks deployment when a degradation is registered in the aggregate Virtual Experience Score based on Web Vitals. Read below for more details. |
Reliability and performance checks run against the automatic deployment URL Vercel generates. In case of failures or degradations, what actually gets blocked is the deployment to all other URLs, e.g. branch URLs and user-assigned domains.
Virtual Experience Score & Web Vitals
Together with the team at Vercel, we developed the Virtual Experience Score (VES) that gives you one simple KPI to track.
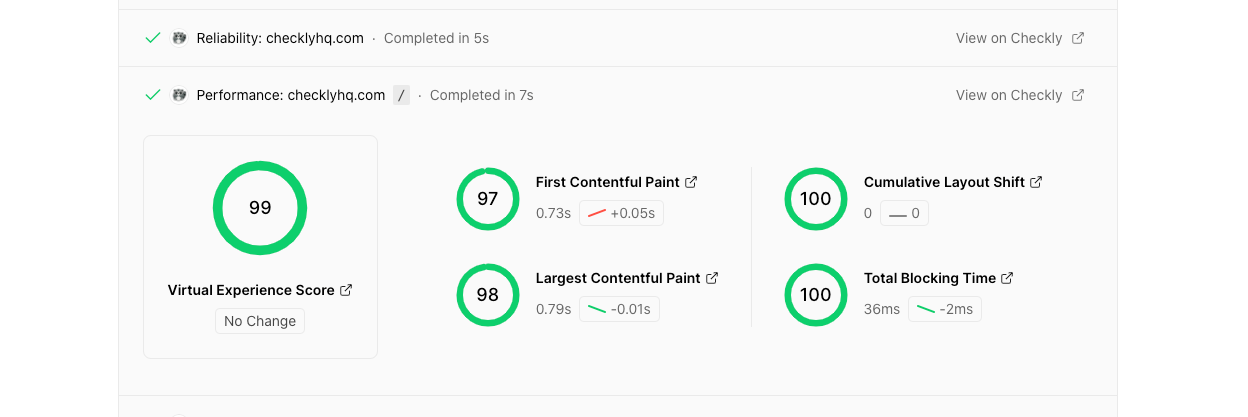
The Virtual Experience Score does three things:
- It aggregates your Web Vitals metrics into one number from 0 to 100, just like you might have seen with Lighthouse scoring.
- It assigns a “weight” to each score, marking its impact on your UX.
- It chops up the score into the top 10% (p10), the top 50% (median) and the rest.
In the table below you can see the exact numbers and their weight in the Virtual Experience Score.
| Web Vitals metrics | p10 / 90% | median / 50% | weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCP | 934ms | 1600ms | 0.20 |
| LCP | 1200ms | 2400ms | 0.35 |
| TBT | 150ms | 350ms | 0.30 |
| CLS | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
So, what does this mean for the blocking heuristics? It means that we will mark a check as blocking when:
- A check reports web vitals, and…
- The VES has degraded in relation to the last available Production deploy. Degraded means they passed the range threshold, i.e from p10 to median.
For more info on the Virtual Experience Score check the documentation on the Vercel site.
Skipping Performance checks
In some cases, Checkly will completely skip performance checks. You will see the “skipped” status in your Vercel deployment overview. Checkly skips performance checks when the domain of the visited URL in the script does not match the domain of the deployment URL. In 9 out of 10 cases this should be the URL for your Preview and Production deployments.
Vercel-linked check results
When selecting a check which is linked to a Vercel project, any results triggered by a deployment on that project will show at the bottom of the check page, under the tab CI/CD triggered check results.
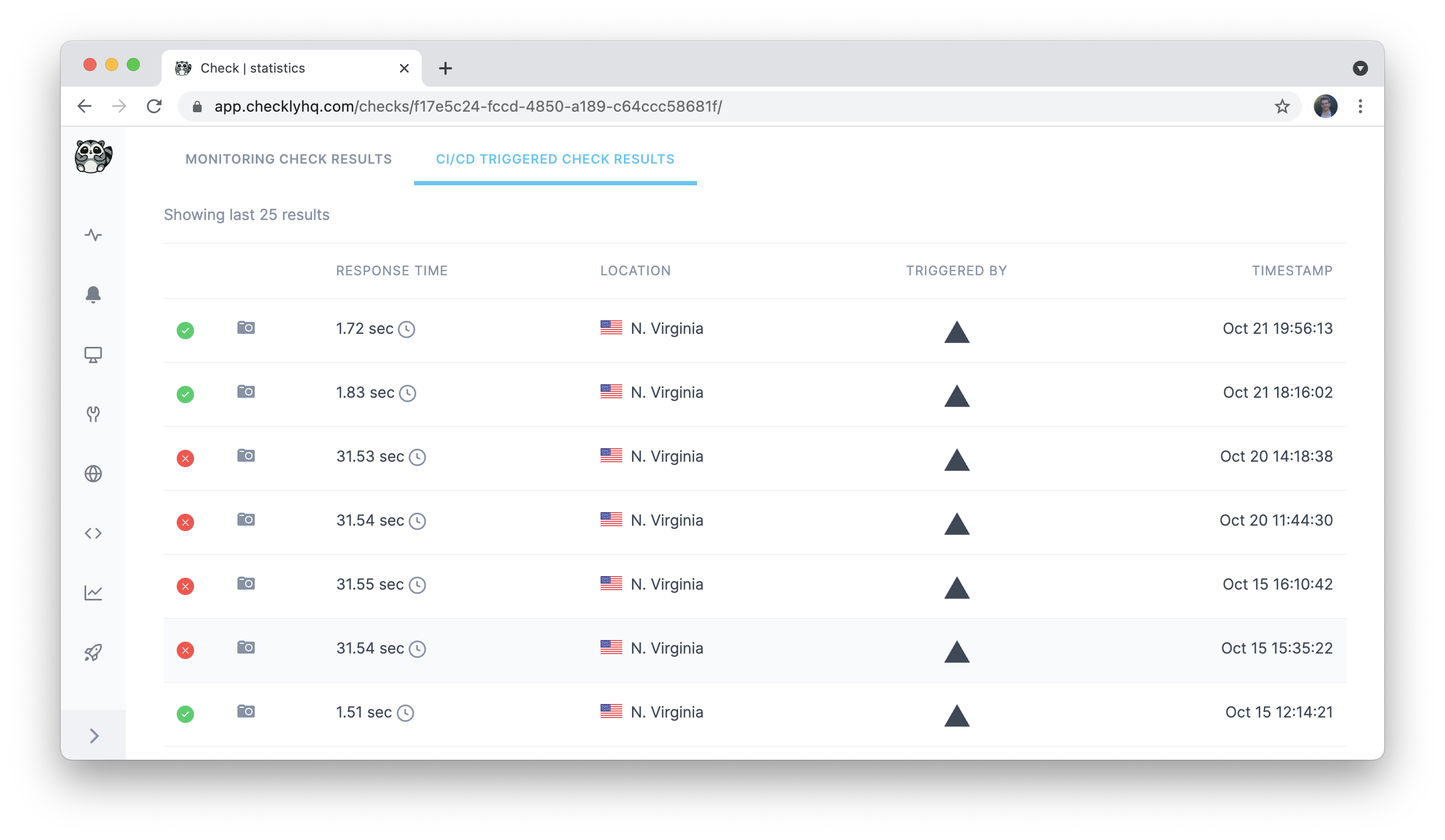
On Vercel, you will also see a breakdown of checks that were executed on a given deployment, together with a breakdown of various key web vitals.
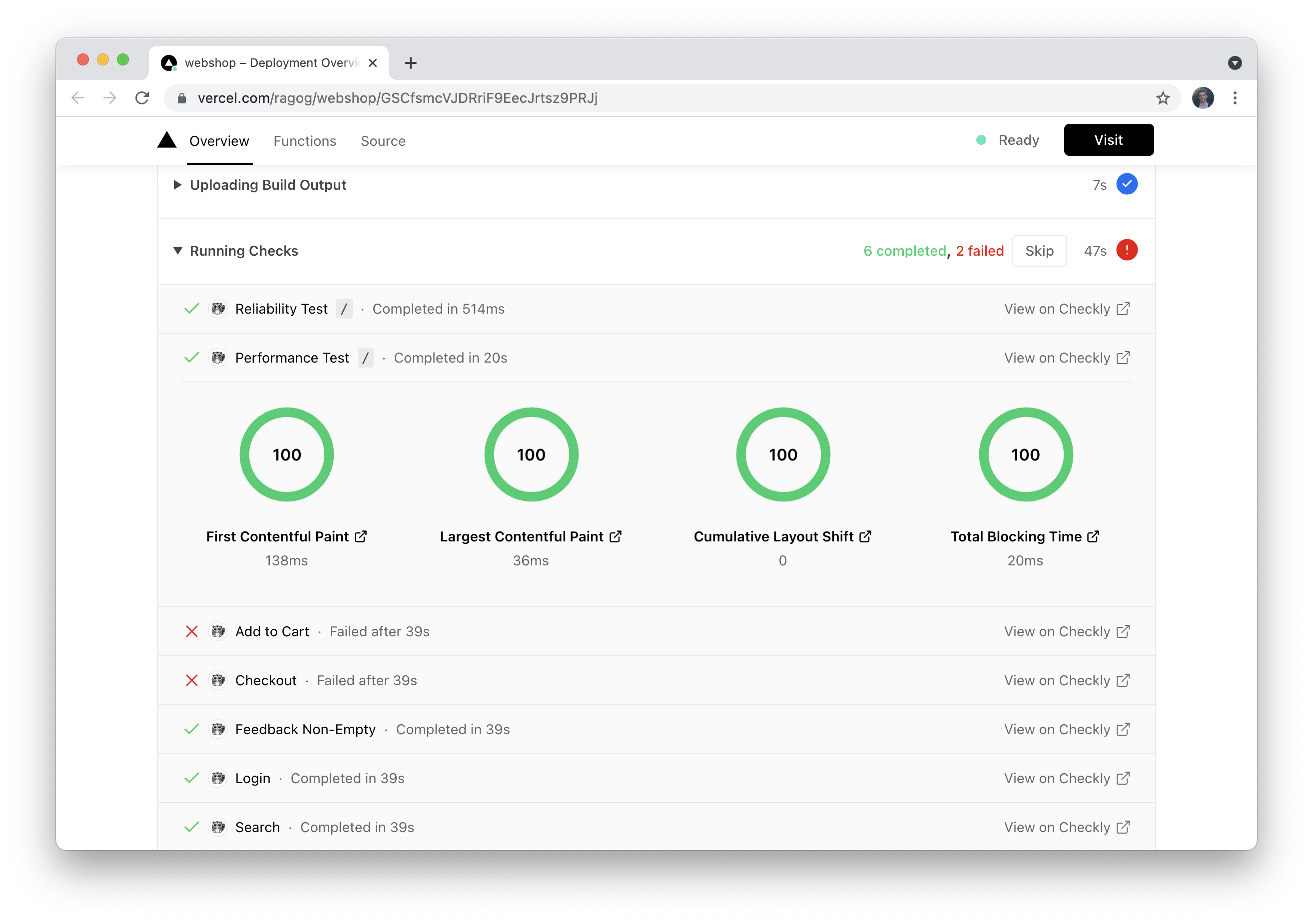
Web vitals are available for Playwright-based browser checks using runtime 2021.06 or newer.
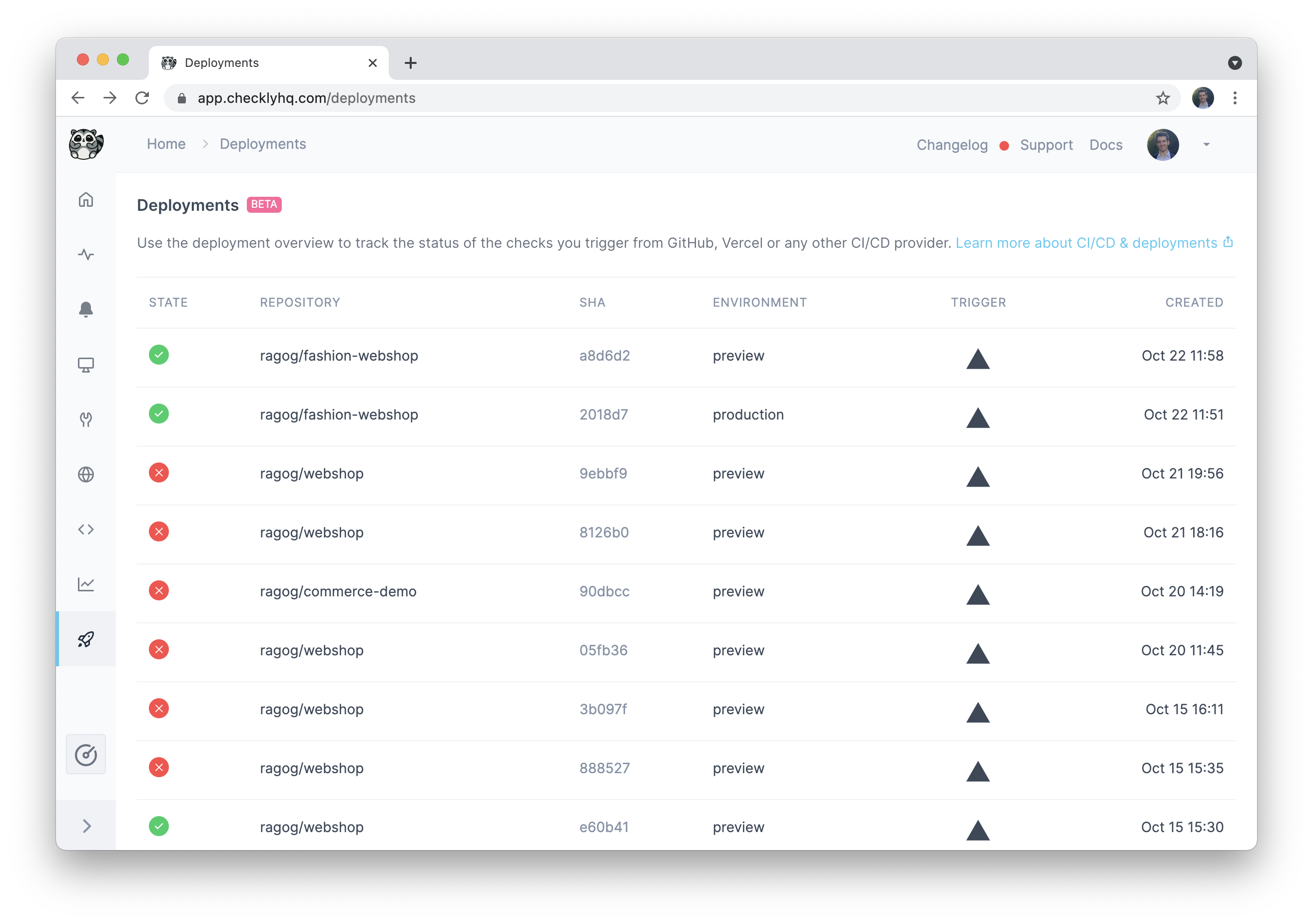
Deployments tab
The Deployments tab lists all deployments on linked projects, including Vercel-based ones, together with the check executions they triggered.
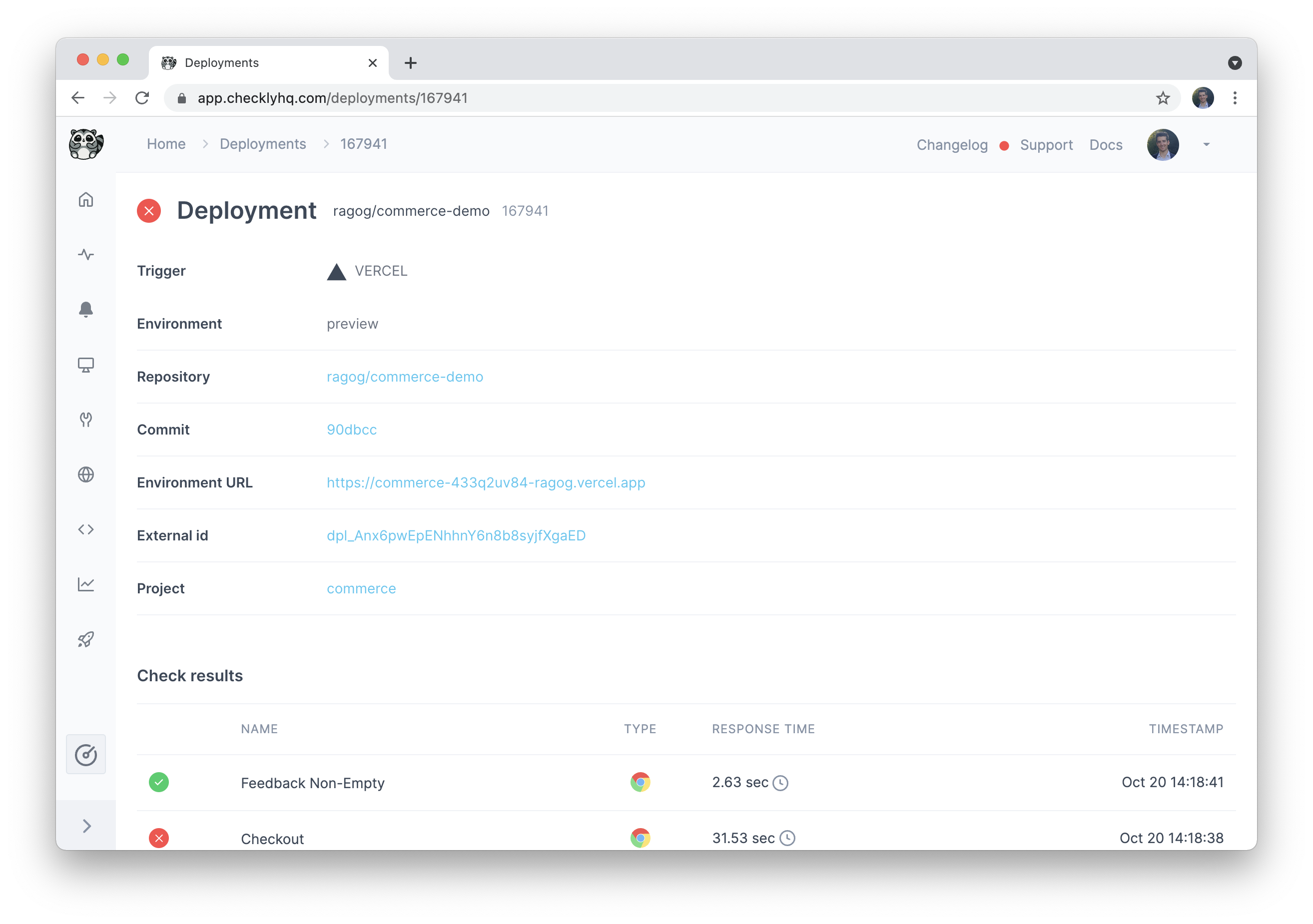
Selecting a deployment enables you to quickly determine whether it caused any check failures, and to drill into the relevant information in case it did.
Last updated on February 5, 2025. You can contribute to this documentation by editing this page on Github